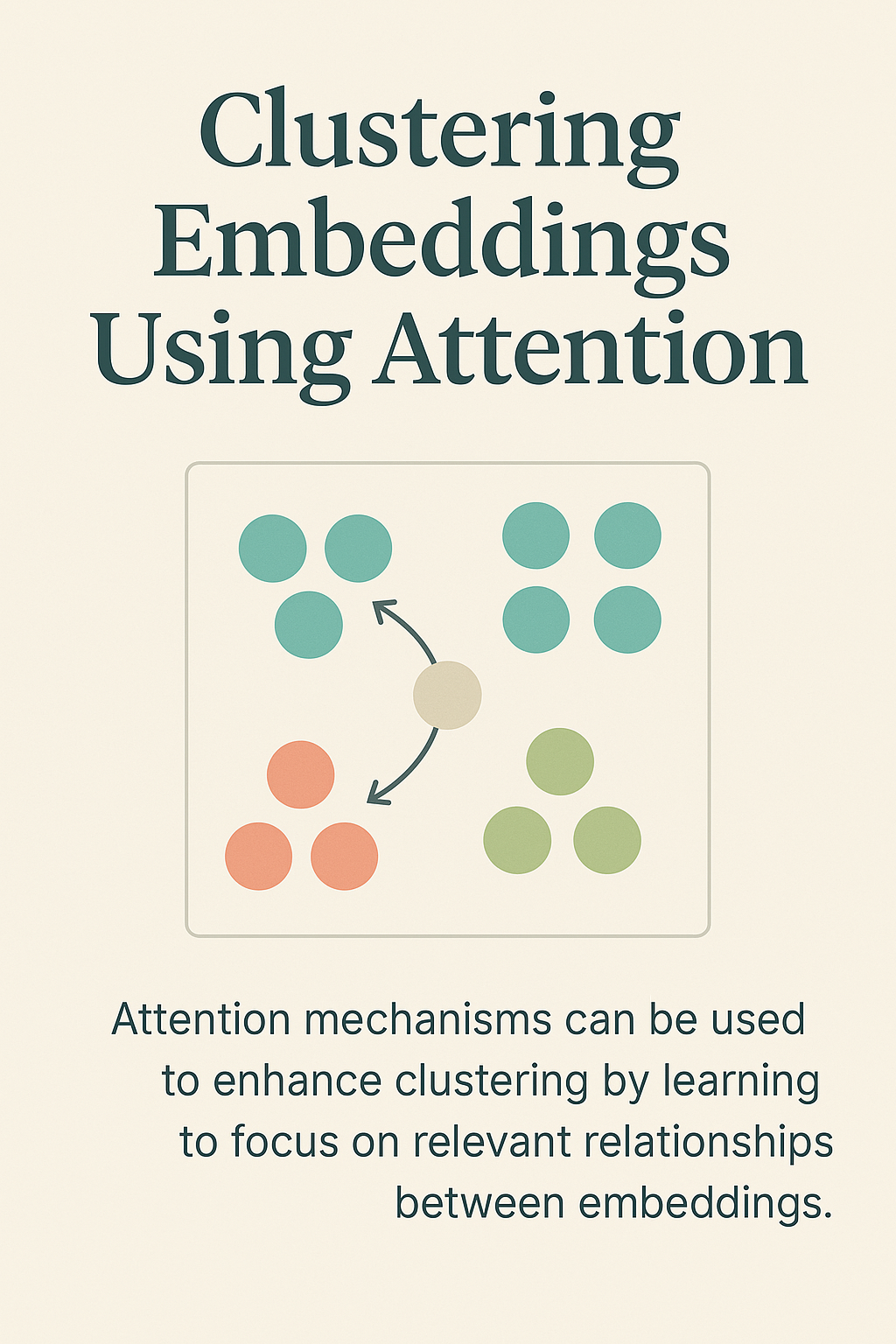
Clustered Embedding Using Attention
Developing a Novel Embedding Space via Attention-Guided Clustering
Clustered Embedding Using Attention
Project Overview
In this project, we explore a novel approach to word embedding that departs from traditional predictive objectives. Instead of relying on pre-trained models tuned for next-token prediction, we start with uniformly distributed, maximally distant embeddings and update them exclusively based on attention signals extracted from BERT. Our goal is to create an embedding space where similar words naturally cluster together based on their contextual relationships—guided solely by attention.
Purpose
Why Clustered Embeddings?
Standard embeddings (like those from Word2Vec or BERT) are optimized for language modeling tasks. While powerful, these embeddings often carry inherent biases and may not explicitly capture the semantic grouping desired for specific downstream applications. Our approach emphasizes:
- Contextual Clustering: By using attention signals from detailed word descriptions, embeddings only move closer when contextually justified.
- Preserving Distinctiveness: Starting with a uniformly distributed, maximally distant space prevents collapse and ensures each word retains its uniqueness.
- Task Adaptability: The resultant clustered embeddings can later be integrated into more complex systems, enhancing tasks like semantic search or downstream NLP applications.
Key Features
Data Preparation & Precomputation
- Cleaned Descriptions: Raw JSON data containing word descriptions is cleaned and consolidated into a standardized format.
- Attention Precomputation: BERT is used to extract token-level attention scores for each description. These scores, along with tokenized representations, are precomputed and stored for efficiency, ensuring that the training pipeline is not burdened with real-time attention extraction.
Uniform Embedding Initialization
- Maximally Distant Start: We initialize our embedding space with uniformly distributed vectors on a unit hypersphere. This guarantees that every word starts maximally distant from one another, setting a neutral baseline for subsequent clustering.
- Trainable Space: The custom embedding module is designed to be updated solely by context, ensuring that only words with strong attention signals are moved closer together.
Attention-Based Updates
- Contrastive Learning with Negative Sampling: A gated MLP selectively updates embeddings by drawing them closer to their attention-weighted context representation while pushing apart embeddings from unrelated contexts.
- Gated Update Mechanism: The update function ensures that embeddings move only towards related contexts, preventing arbitrary shifts and preserving the integrity of the initial uniform distribution.
Challenges and Solutions
Achieving Effective Clustering
- Challenge: Without the traditional language-modeling objective, embeddings might not naturally group by semantic similarity.
- Solution: We employ a contrastive loss framework that rewards moving embeddings closer to contexts with high attention signals, and penalizes them for being too close to irrelevant (negative) contexts.
Precomputation Efficiency
- Challenge: Running BERT for each word-description pair on the fly is computationally prohibitive.
- Solution: By precomputing and storing attention scores along with tokenized representations and initial embeddings, our training loop becomes significantly faster and more scalable.
Results
Preliminary experiments show promising results:
- Semantic Grouping: Similar words begin to cluster together as training progresses, reflecting the attention-based signals from their descriptions.
- Training Efficiency: Precomputation has reduced runtime overhead, allowing for faster iterations and experimentation.
- Robust Loss Dynamics: The contrastive loss successfully balances pulling related embeddings together while maintaining clear boundaries for dissimilar words.
Future Work
Enhanced Aggregation Techniques
We plan to explore multi-level (tertiary) aggregation of attention scores across multiple descriptions per word, providing even finer-grained update signals.
Integration with Downstream Tasks
The next step is to integrate these clustered embeddings into broader NLP applications—such as semantic search, document clustering, or even as an initialization for further fine-tuning in large language models.
Visualization and Analysis
Future iterations will include interactive visualization tools (e.g., t-SNE, UMAP) to monitor the evolution of the embedding space and validate the effectiveness of our attention-guided clustering.
Conclusion
Clustered Embedding Using Attention represents a fresh perspective on embedding learning. By divorcing the update process from traditional predictive tasks and focusing solely on contextual relationships derived from attention, we are able to form an embedding space that is both semantically meaningful and highly adaptable. This project lays the groundwork for future innovations in embedding techniques and their applications across various NLP tasks.
Repository and Resources
For full implementation details, code, and additional documentation, visit the project repository: